[ 7.10.5 amd64 trusty ]
[ 8.2.3 amd64 trusty ]
[ 8.2.3 amd64 xenial ]
abinit-psp
[ 2 all ]
abinit-psp-jth (pawxml)
[ 1.0 all ]
abinit-psp-gbrv (paw)
[ 1.5 all ]

http://www.abinit.org/
Compiled with OpenMPI, OpenMP, and msym = 10368 to allow 6x6x6 supercells.
This psp package contains a full set of pseudopotentials, as gathered by ASE.
The installation location of pseudo potentials is in /usr/share/abinit/psp
X. Gonze et al, Computer Physics Communications 180, 2582-2615 (2009).
We recommend that you install the abinit-psp-jth, abinit-psp-gbrv and abinit-psp pseudo potentials.
[ 1.9.14 amd64 ]
https://www.scripps.edu/tainer/arvai/adxv.html
Many common detector and data formats are recognized, including: ADSC Mar ccd Mar image plate (old and new format) Raxis II & IV Crystallographic Binary Format (CBF) XDS .pck files European Data Format (EDF) Numerical Python (NUMPY) Hierarchical Data Format (HDF5) Tagged Image File Format (TIFF) Raw binary integer and floating point data
Adxv is freely available to everyone. There is no registration, license or fee required to use it.
[ 1.8.0 amd64 trusty ]
http://bigdft.org/
Pseudo potentials are included in the package. Tutorials and Manuals are in /usr/share/doc/bigdft.
On a multicore machine (SMP) you do not need MPI, as OpenMP will use available CPU's. Just launch 'bigdft', not 'mpirun -np N bigdft'.
L. Genovese et al, J. Chem Phys 129 014109 (2008)
This package is built with OpenMPI and OpenMP support.
[ 0.9.1 amd64 ]
[ 1.3.0 amd64 ]
http://apps.jcns.fz-juelich.de/BornAgain
by C. Durniak, G. Pospelov, W. Van Herck, J. Wuttke
License: GPL3
The installation location is /usr/local/BornAgain
[ 1.15 amd64 ]
https://www.cgl.ucsf.edu/chimera/
License: UCSF
UCSF Chimera is a program for the interactive
visualization
and analysis of molecular structures and related data,
including density maps, trajectories, and sequence
alignments.
It is available free of charge for noncommercial use.
Install location is /opt/UCSF
We encourage Chimera users to try ChimeraX for much better performance with large structures, as well as other major advantages and completely new features. Chimera is no longer under active development.
[ 1.2_amd64 ]
by E. Farhi
License: EUPL
* CrysFML by Juan Rodriguez-Carvajal and Javier Gonzalez-Platas, ILL and ULL, Tenerife, Spain (LGPL 3.0)
* Commission on Crystallographic Computing, IUCr Newsletter No.1, pp 50-58,
January 2003
* McStas: K. Lefmann and K. Nielsen, Neutron News 10, 20, (1999) ; P. Willendrup, E. Farhi and K. Lefmann, Physica B, 350 (2004) 735.
To use the software, launch 'cif2hkl' from a Terminal. Installation is in /usr/local/cif2hkl
A web service also exists at <http://barns.ill.fr/cif2hkl.html>
[ 4.1 amd64 trusty xenial ]
Warning: We recommend you also upgrade the cp2k-data with the release 4.1 from here.

by CP2K developers group
https://www.cp2k.org/
License: GPL 2
https://www.cp2k.org/
This debian distribution is built with Scalapack, Blacs, openMPI.
[ 2.7 amd64 ]
pseudo-potentials
[ 2 all ]

by DTU Fysik, Copenhagen
License: GPL2
https://wiki.fysik.dtu.dk/dacapo/
To use the software, use dacapo_serial.run or through ASE (apt://python-ase).
B. Hammer et al, Phys.Rev. B 59, 7413 (1999).
[ 2.3 amd64 ]
http://www.ncnr.nist.gov/dave/
by Richard Azuah, NIST
License: NIST
The main objective of DAVE is to provide a user friendly tool for scientists involved in neutron scattering research to quickly reduce, visualize and interpret their data. Currently, much progress has been made towards achieving this goal even though a lot still remains to be done. Support for several neutron scattering spectrometers at NCNR and PSI is included.
DAVE: A comprehensive software suite for the reduction, visualization, and analysis of low energy neutron spectroscopic data, R.T. Azuah, L.R. Kneller, Y. Qiu, P.L.W. Tregenna-Piggott, C.M. Brown, J.R.D. Copley, and R.M. Dimeo, J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stan. Technol. 114, 341 (2009).
The installation location is /usr/local/dave
[ 1.10 amd64 xenial ]
https://www.scd.stfc.ac.uk/Pages/DL_POLY.aspx
by W. Smith, T.R. Forester and I.T. Todorov
License: STFC
Users of the package are referred to the User Manual supplied.
This is the OpenMPI version. The 'gopoly' command will launch DL_POLY with 4 cores, or use 'mpirun -np NP DL_POLY.X'.
The dl-gui command will launch a GUI.
Data files (examples) are in /usr/share/dlpoly/data and documentation in /usr/share/doc/dlpoly
[ 160415 amd64 ]
https://github.com/biochem-fan/eiger2cbf
[ 4.3.6 amd64 trusty ]
[ 4.3.6 amd64 xenial
[ 6.2.8 bionic ]

http://elk.sourceforge.net/
License: GPL3
WARNING: the efficiency is good with either OpenMP OR OpenMPI, not both. Use commands:
- with MPI: OMP_NUM_THREADS=1 mpirun -n 8 elk-lapw ...
- with OpenMP: elk-lapw ...
Elk is an all-electron full-potential linearised augmented-plane wave (FP-LAPW) code. By not including pseudo-potentials, Elk can provide very reliable high-precision results and works for every chemical element. Features include:
* FP-LAPW basis with local-orbitals
* APW radial derivative matching to arbitrary orders at muffin-tin surface (super-LAPW, etc.)
* Arbitrary number of local-orbitals allowed (all core states can be made valence for example)
* Total energies resolved into components
* LSDA and GGA functionals available
* Isolated molecules or periodic systems
* Core states treated with the radial Dirac equation
Elk is parallelized via OpenMP and MPI. Using OpenBLAS.
This version has been compiled with elk/src/modmain.f90:289 maxsymcrys=10368 to handle 6x6x6 supercells.
[ 13.11 amd64 ]
http://www.ill.fr/tas
by Paul Steffens <steffens@ill.eu>
License: GPL3
To start the flatcone, type 'plotmultiple file' at the prompt.
Any Matlab expression/command can, also be entered.
The installation location is /usr/local/flatcone, which contains 'doc' and 'examples'
The main command for using FlatCone is 'plotmultiple'.
To use this software, you need to install the Matlab Compiler Runtime in /opt/MATLAB,
so that you should have a directory /opt/MATLAB/MATLAB_Compiler_Runtime/v713/.
If you install the MCR in an other location, assign the MCRROOT env variable to
its location.
Refer to <http://www.ill.fr/tas> for on-line documentation.
Matlab is a registered trademark of The Mathworks Inc.
[ 2.1.8 amd64 ]

http://apps.jcns.fz-juelich.de/doku/frida/start
by Joachim Wuttke <j.wuttke@fz-juelich.de>
License: GPL3
It has been written for the analysis of inelastic neutron scattering data, and it contains highly specialized routines for this purpose. Its data model, however, is abstract and generic so that Frida can be applied to whatever data of the form y(x,z0,z1,...).
Frida's main capabilities are:
Import/export tabular data from/to various formats.
Reorganize, bin, sort, clone data.
Perform mathematical operations on the data.
Automatically document all data manipulations.
Fit the data with user-defined functions.
Plot data and functions, generating publication-grade PostScript graphics.
Besides, Frida is also a powerful pocket calculator.
Frida is operated through a command-line interface. Commands are cryptic. Everything is designed to offer a maximum of computational power and flexibility for a minimum of typing. Learning Frida is not easy, but rewarding.
Some example data files and documentation is available in /usr/local/share/frida
[ 13.10 amd64 ]

https://www.ill.eu/sites/fullprof/
by Juan Rodriguez-Carvajal <fullprof@ill.fr>
License: Unspecified (ILL,LLB)
The different programs can be run either in stand alone form (from a console window or clicking directly in a shortcut) or from the interfaces WinPLOTR and/or EdPCR.
The programs within the FullProf Suite are distributed in the hope that they will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY of being free of internal errors. In no event will the authors (or their institutions) be liable to you for damages, including any general, special, incidental or consequential damages arising out of the use or inability to use the programs (including but not limited to loss of data or data being rendered inaccurate or losses sustained by you or third parties or a failure of the program to operate with any other programs). The authors are not responsible for erroneous results obtained with the programs.
The installation location is /usr/local/fullprof
To start the FullProf toolbar, use 'tfp'
[ 10.05 amd64 bionic ]
[ 10.05 amd64 xenial ]

https://geant4.web.cern.ch/
License: Geant4 Software License
Installation location in /usr/local/geant4.10.05
Start with;
- cd /tmp; mkdir B1-test; cd B1-test/
- cmake /usr/local/geant4.10.05/share/Geant4-10.5.1/examples/basic/B1/
- make
- ./exampleB1
[ 2.4.1 amd64 ]

http://genx.sourceforge.net/
by Matts Bjorck <Matts.Bjorck@gmail.com>
License: GPL3
The installation location is /usr/local/genx
[ 0.10.0 amd64 trusty 1.2 amd64 trusty 1.2_amd64_xenial ]
gpaw-setups
[ 0.9 all ]

https://wiki.fysik.dtu.dk/gpaw/
J. J. Mortensen et al, Phys Rev B, Vol. 71, 035109 (2005).
[ 6.87 amd64 ]

https://www.ill.eu/users/support-labs-infrastructure/software-scientific-tools/grasp/
by Charles Dewhurst <dewhurst@ill.fr>
License: Unspecified (ILL)
The installation location is /usr/local/grasp, which contains documentation.
Examples can be found at http://www.ill.eu/instruments-support/instruments-groups/groups/lss/grasp/example-data
To use this software, you need to install the Matlab Compiler Runtime in /opt/MATLAB, so that you should have a directory /opt/MATLAB/MATLAB_Compiler_Runtime/v713/.
If you install the MCR in an other location, assign the MCRROOT env variable to its location.
[ 1.1188 amd64 ]
http://www.ncnr.nist.gov/xtal/software/gsas.html
by Allen C. Larson and Robert B. Von Dreele, B. H. Toby
License: NIST
GSAS has been created by Allen C. Larson and Robert B. Von Dreele of Los Alamos National Laboratory. Executable versions of GSAS are distributed more-or-less freely (see the friendly message from the Regents of the University of California, below), but the source code is not distributed (don't complain to me on this one, I agree with you).
The installation location is /usr/local/gsas
[ 3.1.0 amd64 ]
License: HDF Group
https://www.hdfgroup.org/downloads/hdfview/
The official Debian package (2.9) can not read recent HDF
files.
HDFView is a visual tool written in Java for browsing and editing HDF (HDF5 and HDF4) files. Using HDFView, you can:
View a file hierarchy in a tree structure
Create new files, add or delete groups and datasets
View and modify the content of a dataset
Add, delete and modify attributes
HDFView uses the Java HDF Object Package, which implements HDF4 and HDF5 data objects in an object-oriented form.
[ 2.13.11 amd64 ]

http://horace.isis.rl.ac.uk/Main_Page
by Toby Perring <toby.perring@stfc.ac.uk>
License: ISIS
of large datasets from time-of-flight neutron inelastic scattering spectrometers.
To start Horace, use: horace
Example files are included in the software, and can be used with e.g. 'demo_script'
The installation location is /usr/local/horace
To use this software, you need to install the Matlab Compiler Runtime in /opt/MATLAB, so that you should have a directory /opt/MATLAB/MATLAB_Compiler_Runtime/v713/.
If you install the MCR in an other location, assign the MCRROOT env variable to its location.
Refer to <http://horace.isis.rl.ac.uk> for on-line documentation.
Matlab is a registered trademark of The Mathworks Inc.
http://idl2matlab.sourceforge.net/
Coordinators: Didier Richard <richard(at)ill.eu> and Emmanuel Farhi <farhi(at)ill.fr>
License: GPL2
An automatic translator from IDL to
Matlab and Scilab.
The translation performs an IDL syntax check, and reports
possible warnings and errors into a Log.
This library is quite big, and covers the most useful
IDL/Matlab functions, particularly mathematical functions,
basic plotting functions, widgets/uicontrols
Refer to http://idl2matlab.sourceforge.net/
A web service also exists at <http://barns.ill.fr/idl2matlab.html>
[ 1.10 amd64 ]
[ 2.0 amd64 ]
[ 2.0.2 amd64 ]
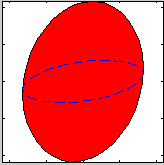
http://ifit.mccode.org
by Emmanuel Farhi <farhi@ill.fr>
License: EUPL (GPL)
The iFit program provides a set of methods to load, analyze, plot, fit and optimize models, and export results. iFit is based on Matlab, but stand-alone version does not require a Matlab license to run. Any text file can be imported straight away, and a set of binary files are supported. Any data dimensionality can be handled, including event based data sets.
The spirit of the software is to include simple object definitions for Data sets and Models, with a set of methods that provide all the means to perform the usual data analysis procedures.
- iData objects to hold data sets ; Import with: iData('filename')
- iFunc objects to hold models ; Create new ones with: iFunc('expression')
- fit model to data with: fits(data, model)
- documentation is available in /usr/local/share/doc/ifit
You can not define new Matlab functions in this stand-alone release, but can define new iFunc objects to hold your function body.
Main functionalities are: [ iData Load Plot Math Fit Save Optimization iFunc Models ]
Contains special hooks with McStas, and computation of Phonons as well as ResLibCal.
To use this software, you need to install the Matlab Compiler Runtime in /opt/MATLAB, so that you should have a directory /opt/MATLAB/MATLAB_Compiler_Runtime/v713/. If you install the MCR in an other location, assign the MCRROOT env variable to its location. This step can be automated by selecting the MCRInstaller package.
To start iFit, use: ifit
Refer to <ifit.mccode.org> for on-line documentation.
Matlab is a registered trademark of The Mathworks Inc.
E. Farhi, Y. Debab and P. Willendrup, J. Neut. Res., 17 (2013) 5. DOI: 10.3233/JNR-130001
[ 1.10_amd64 ]
Includes: openmpi-bin, libxc1, libnetcdf-dev, phon, quantum-espresso-sssp, quantum-espresso, abinit-psp, abinit-psp, abinit-doc, abinit, python-matplotlib, gpaw-setups, gpaw, elk-lapw, ifit
To use this tool, start iFit, then type: help sqw_phonons
[ 1.9 all ]
[ 2.0.0 all ]
Once installed, access these services from a web browser at e.g. http://localhost/ifit-web-services
[ 1.9.1.18 amd64 ]
http://ftp.sns.gov/ISAW/
by Dennis Mikkelson <mikkelsond@uwstout.edu>
License: GPL2
Reference: J. Tao et al, NIMA 422 (2006) 562
The installation location is /usr/local/isaw
[ 15.02 amd64 ]
[ 18.05 amd64 ]
https://www.ill.eu/users/support-labs-infrastructure/software-scientific-tools/lamp/
by Didier Richard <lamp@ill.fr>
License: ILL
LAMP provides a predictable and intuitive graphical user interface which integrates scientific visualisation with an enhanced data language. Many high level modules are predefined to enable interactive data analysis and visualisation of 2D , 3D data and atomistic representations.
LAMP also provides:
Input and output of various data-type files with CUSTOMIZED MODULES.
Expansion and simplification of data with USER-MACROS in Interactive Data Language IDL.
General fitting interfaces for 2D and SIMULTANEOUS FITS with CONSTRAINTS.
Visualisation of calculated PHONONS and molecular VIBRATIONS.
Cristal and Magnetic STRUCTURES with propagation vectors EDITOR.
Miller planes in the CRYSTALLOGRAPHIC CELL easily animated to help visualise local structure.
RECIPROCAL SPACE densities calculated from multiple instrument acquisition scans.
Automatic ELECTRONIC LOG BOOKS updated in html format by a right click on images.
Lamp , Nxml , NeXuS FILE BROWSER with snapshot images.
Direct link to a powerful IMAGE-MANIPULATION module, Scan.
The live control of an experiment with GEORGE.
The same behaviour on Unix Motif platforms, MS_windows, MacIntosh.
A distribution package for the scientific community with a FREE embedded IDL license.
A LIVE-UPDATE feature to keep your application always up-to-date.
Reference: D. Richard, M. Ferrand and G.J. Kearley, J. Neutron Research 4, 33-39, 1996.
The installation location is /usr/local/lamp, which contains documentation.
[ 1.4 amd64 ]
<http://looktxt.sourceforge.net/>
[ 7.13 amd64 ]
http://www.mathworks.com
This package is needed to execute any Matlab compiled application (stand-alone) such as iFit <ifit.mccode.org>, grasp, flatcone, ...
Matlab is a registered trademark of The Mathworks Inc.
Packaged by E. Farhi, ILL.
[ 2.2 amd64 ]
[ 2.3-py amd64 ]
[ 2.3-perl amd64 ]

http://mcstas.org/
by P. Willendrup, E. Knudsen, K. Lefmann, E. Farhi, U. Filges <mcstas-users@mcstas.org>
License: GPL
McStas is based on a compiler that reads a high-level specification language defining the instrument to be simulated and produces C code that performs the Monte Carlo Simulation. The system is very fast in use, both when setting up the instrument definition and when doing calculations. Typical figures are 500000 neutron histories per second on a fast PC.
McStas supports triple-axis, time-of-flight
instruments, and polarised neutrons. It comes with a
comprehensive manual and a library of well-tested
components that include most standard elements of neutron
scattering instruments, including steady-state and pulsed
sources, monochromators/analysers, guides, collimators,
vanadium and powder samples, velocity selectors and
choppers, and a variety of detectors.
- K. Lefmann and K. Nielsen, Neutron News 10, 20, (1999).
- P. Willendrup, E. Farhi and K. Lefmann, Physica B, 350 (2004) 735.
[ 1.2 amd64 ]
http://mcxtrace.org/
by E. Knudsen <mcxtrace-users@mcxtrace.org>
License: GPL
It is a collaborative effort between DTU Physics, European Synchrotron radiation Facility, Niels Bohr Insitute. Initial funding came from a grant under the NaBiIT program of the Danish Strategic Research Council DSF and from SAXSLAB ApS, in addition to the above parties.
It is built upon the code base of the proven and succesful neutron ray-tracing package McStas and today McXtrace and McStas share a central code repository.
A substantial amount of work has gone into creating this software package. If you enjoy it, and use it for your work please use this reference:
- E Bergback Knudsen, Andrea Prodi, Jana Baltser, Maria Thomsen, P Kjer Willendrup, M Sanchez del Rio, Claudio Ferrero, Emmanuel Farhi, Kristoffer Haldrup, Anette Vickery, et al. Mcxtrace: a monte carlo software package for simulating x-ray optics, beamlines and experiments. Journal of Applied Crystallography, 46(3):679-696, 2013.
[ 1.2 amd64 trusty ]
[ 1.2 amd64 xenial ]
[ 1.3 amd64 trusty/xenial/bionic ]
https://mdanse.org/
License: CeCILL
code at https://code.ill.fr/scientific-software/mdanse
This distribution includes the Molecular Modelling Toolkit (MMTK), a library which contains a wide range of algorithms that are used in molecular simulations and modelling. It is particularly useful for data analysis and visualization, but also contains standard techniques such as energy minimization and Molecular Dynamics.
The installation location is /usr/local/mdanse. Example files are in /usr/share/doc/mdanse.
Packaged by E. Pellegrini, ILL.
cite: J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2017, 57, 1−5 - DOI: 10.1021/acs.jcim.6b00571
[ 4.3.3 amd64 ]
Warning: deprecated. We recommend you rather use ifit instead (see above).

http://www.ill.eu/instruments-support/computing-for-science/cs-software/all-software/matlab-ill/
by Emmanuel Farhi <farhi@ill.fr> and others
License: GPL
provides an attractive and easy to use point-and-click interface. Most operations (including guessing starting parameters for fits) can be performed via the mouse. The main object is to fit any type of (x,y) data with any fit function (even combinaisons), with various efficient algorithms. Many options are also available. A full manual is available at <http://www.ill.eu/instruments-support/computing-for-science/cs-software/all-software/matlab-ill/mfit/home/>
Mview (now v4.2.2, Aug 22nd 2005) - refer to iFit for a more recent implementation
is designed in order to manipulate and display up to 20 data files. As Mfit, it is also a point-and-click application. A link with MFit permits to fit each data set.
Rescal (now v5.1) - refer to ResLibCal for a more recent software
is a specific application to compute 4D resolution ellipsoid for inelastic scattering instruments (neutrons... Popovici's and Cooper Nathan's methods). It is then possible to use it through a 4D convolution in a fit function (see "trix", which is included in archives).(note : this program is not based on "Rescal" famous code). A full manual is available at <http://www.ill.eu/instruments-support/computing-for-science/cs-software/all-software/matlab-ill/rescal-for-matlab>
The installation location is /usr/local/mfit_mview
Warning: deprecated. We recommend you rather use ifit instead (see above).
[ 1.0.1 amd64 ]

https://www.ill.eu/neutronencyclopedia/
by A. Filhol <filhol@ill.fr>
License: Artistic
However, it is important to note that the project was never finished and iMediaSoft published a version that lacks many corrections.
Topics from the content: Science:
* The neutron, Neutrons and states of matter; Internal motions of matter; Magnetism; Nuclear physics; Materials. Neutron Sources:
* Natural sources; Transportable sources; High flux sources; Sources of the future; Miscellaneous. Tools for neutron science: Neutron activation; Transmission imaging; Diffraction; Small-angle scattering; Reflectometry; Inelastic scattering; Quasielastic scattering; Spin echo; Isotopic substitution; Neutron holography; Recoil and gamma spectrometry; neutrons optics; Neutron detection; Sample environment Applications
The multimedia encyclopedia "Exploring matter with neutrons" was created by Alain FILHOL (main author, Institut Laue-Langevin) and Dan BOG (developer and editor through iMediaSoft & Nanopolis). Today the "Exploring matter with Neutrons" encyclopedia is reproduced here with permission of Alain FILHOL and Dan BOG.
Installation location is /opt/ILL/NEUTRON-ENCYCLOPEDIA
[ 2.6.1 amd64 ]

https://www.ill.eu/neutrons4science/
by Alain Filhol <filhol@ill.fr>
License: ILL, Ipter
Neutrons and protons are elementary particles constituting the nucleus of atoms. The neutron has no electric charge but has a spin and a magnetic moment. Neutron beams - like beams of X-rays, electrons or muons - are valuable tools for studying the multitude of materials that surround us in our daily lives (alloys, magnets, superconductors, polymers, colloids, proteins, biological systems, ...). However, the way neutrons interact with matter is quite unique and, as a result, it can often reveal to us what is normally hidden. With Neutrons4Science you can discover one of the many types of neutron spectroscopy.
The neutron also answers questions on the very foundations of physics, helping us to solve some of the great mysteries of the universe (Is the Grand Unified Theory valid? Is there a fifth fundamental force? ...) As an example, Neutrons4Science gives you insights to a brand new method of neutron spectroscopy that takes advantage of the quantum states of this light neutral particle.
Neutrons4Science lets you experience neutron science through three interactive 3D animations:
* ThALES: Use a neutron spectrometer (ThALES) as if you were performing a real experiment.
* Magnons: Discover the spin waves that exist inside magnetic materials and understand how ThALES can observe them.
* GRANIT: Discover an innovative gravitational spectrometer (GRANIT) based on neutron quantum states in a gravitational field."
These three educational animations were developed with the help of scientists at the "Institut Laue-Langevin", one of the world's flagship facilities for neutron science.
The installation location is /usr/local/neutrons4science
[ 3.0.9 amd64 ]
Obsolete: use MDANSE package. Does not run under modern systems.

https://forge.epn-campus.eu/projects/nmoldyn
by K. Hinsen, M.R. Johnson, G. Kneller,E. Pellegrini <pellegrini@ill.fr>
Obsolete: use MDANSE package
This distribution includes the Molecular Modelling Toolkit (MMTK), a library which contains a wide range of algorithms that are used in molecular simulations and modelling. It is particularly useful for data analysis and visualization, but also contains standard techniques such as energy minimization and Molecular Dynamics.
The installation location is /usr/local/nmoldyn.
This project has been renamed MDANSE (see above)
[ 7.1 trusty xenial ]
http://octopus-code.org/wiki/Main_Page
License: LGPL3, GPL2, ...
Pseudo-potentials are provided in /usr/share/octopus
[ 0.5.0 amd64 ]
https://github.com/Quasars/orange-spectroscopy
https://quasar.codes/
License: BSD-like
Freely build visual data analysis workflows that help answer your scientific questions. Combine widgets that share input and output types. There are infinite possibilities!
A whole is always more than the sum of parts. Although our journey started with (hyper)spectral data through the Orange Spectroscopy toolbox, Quasar intends to add file readers, processing tools, and visualizations for multiple measurement techniques. This will allow the discovery of new scientific insights through multimodal data analysis.
Orange is a general purpose machine learning and visualization platform which can be extended. Quasar is a variant of Orange and includes pre-installed toolboxes for scientific data analysis. Another member of the Orange family is Single Cell Orange, specializing in genomics data.
This package provides Orange3 with Quasar/Spectroscopy.
Launch: Quasar from the Dash/Search or 'quasar' command.
[ 1.2.7 amd64 ]
https://github.com/oasys-kit/OASYS1
https://www.aps.anl.gov/Science/Scientific-Software/OASYS
M. S. del-Rio and L. Rebuffi. License: MIT
for optic simulation software used in synchrotron facilities,
based on Orange 3.
This package provides Shadow/XRayLib/SRW in a simplified Orange3 environment. All python libraries are included (virtual env).
Installation is in /usr/local/oasys1env and examples are in /usr/share/doc/orange3-oasys. launch 'oasys' or search for it as an App.
[ 1.40 amd64 ]
[ 1.41 amd64 ]
http://www.homepages.ucl.ac.uk/~ucfbdxa/phon/
by Dario Alfe
Computer Physics Communications 180, 2622-2633 (2009)
[ 0.5 amd64 ]
Xenial 16.04: also install libhdf5-7
http://pyne.io/
pyne-dev@googlegroups.com
Includes MOAB <https://bitbucket.org/fathomteam/moab> and PyTAPS <https://pythonhosted.org/PyTAPS/index.html>.
[ 3.9.1 all 3.14.0 all ]
python-ase-qe-spglib
[ 0.1.16 amd64 ]
https://wiki.fysik.dtu.dk/ase/index.html
ASE is part of CAMPOS, the CAMP Open Source project.
ASE contains Python interfaces to several different electronic structure codes including Abinit, Asap, Dacapo, Elk, GPAW and SIESTA.
This package provides the Python 2 modules.
The ASE-QE package provides an ASE-QuantumEspresso interface. We also recommend to install the abinit-psp abinit-psp-jth abinit-psp-gbrv and quantum-espresso-sssp packages.
[ 0.1.13 all ]
https://pythonhosted.org/hdf5storage/
[ 2019a amd64 (MPI) ]
[ 2019b amd64 (MPI/CUDA) ]
https://gitlab.esrf.fr/mirone/pyhst2
A. Mirone ESRF. License GPL2
Launch:
- pyhst_2_2019b input.par `hostname`,0 (to use 1st GPU)
- pyhst_2_2019b input.par (to use only MPI)
Test the installation with e.g.:
- cd /usr/share/doc/python3-pyhst2-cuda
- python3 nonregression.py
[ 2019.2.6 amd64 ]
http://ftp.esrf.fr/pub/scisoft/PyNX/
V. Favre-Nicolin ESRF
License: CeCILL-B
1. the computing of X-ray scattering using graphical processing units
2. X-ray wavefield propagation (from near to far field)
3. simulation and GPU-accelerated analysis of experiments using the ptychography and coherent diffraction imaging techniques
* J. Appl. Cryst. 44 (2011), 635-640 Fast computation of scattering maps of nanostructures using graphical processing units
Installation resides in:
- /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/PyNX-2019.2.6-py3.6.egg/
Test with command:
- pynx-test.py opencl live_plot
A few example Python Notebooks reside with the documentation and some data set in:
- /usr/share/doc/python3-pynx
[ 1.11.10 all ]
https://atztogo.github.io/phonopy/
togo.atsushi.f40@kyoto-u.jp
Selected features Phonon band structure, phonon DOS and partial-DOS Phonon thermal properties: Free energy, heat capacity (Cv), and entropy Phonon group velocity Thermal ellipsoids / Mean square displacements Irreducible representations of normal modes Quasi-harmonic approximation: Thermal expansion, heat capacity at constant pressure (Cp), Mode Grüneisen parameters Non-analytical-term correction: LO-TO splitting (Born effective charges and dielectric constant are required.) Interfaces to calculators: VASP, VASP DFPT, Abinit, Pwscf, Siesta, Elk, FHI-aims, Wien2k, CRYSTAL Python APIs
Phonon database: A collection of first principles phonon calculations is available as open data at http://phonondb.mtl.kyoto-u.ac.jp/ , where the raw data of phonopy & VASP results are downloaded.
[ 0.7 all ]
you should remove the quantum_espresso-data package, which may conflict and lead simulations to produce strange results.

http://www.quantum-espresso.org/
This package contains a full set of pseudo-potentials PAW/US/NC from the SSSP library accuracy set, version 0.7. DeltaCodes=0.31 meV.
Test calculations have been performed with
kpoints=6; ecut=1500 [eV]; smearing=0.27 [eV]
but the actual values depend on the elements and crystal structure. Suggested settings are specified at http://materialscloud.org/.
P. Giannozzi, et al J.Phys.:Condens.Matter, 21, 395502 (2009).
Pseudo potentials from http://materialscloud.org/ by Ivano E. Castelli
To be used within ASE, we recommend to install the python-ase-qe-spglib package.
[ 15.08 amd64 ]
[ iFit 1.10 amd64 ]
[ iFit 2.0 amd64 ]

http://ifit.mccode.org/Applications/ResLibCal/doc/ResLibCal.html
by Emmanuel Farhi <farhi@ill.fr> and others
License: EUPL
This is part of iFit <http://ifit.mccode.org>.
[ 5.2.4 amd64 ]

http://neutron.ujf.cas.cz/restrax/
by Jan Saroun <saroun@ujf.cas.cz> and Jiri Kulda
License: GPL2
The installation location is /usr/local/restrax.
Java VM must be installed to run this software.
[ 6.18.00 amd64 (bionic) ]
[ 6.18.00 amd64 (xenial) ]

https://root.cern.ch/
Installation goes in /usr/local/root
To start it, search for ROOT as an App.
[ 0.93.5 amd64 ]
https://kur.web.psi.ch/sans1/SANSSoft/sasfit.html
by Joachim Kohlbrecher <joachim.kohlbrecher at psi.ch>
License: GLP3
The installation location is /usr/local/sasfit
[ 2.2.1 amd64 (old) ]
http://www.sasview.org/
by Mathieu Doucet <doucetm@ornl.gov>
License: GPL3
The installation location is /usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sasview
[4.0.1 trusty xenial ]

SIESTA is both a method and its computer program implementation, to perform efficient electronic structure calculations and ab initio molecular dynamics simulations of molecules and solids.
https://departments.icmab.es/leem/siesta/
License: GPL 3
The possibility of treating large systems with some first-principles electronic-structure methods has opened up new opportunities in many disciplines. The SIESTA program is distributed freely to academics and has become quite popular, being increasingly used by researchers in geosciences, biology, and engineering (apart from those in its natural habitat of materials physics and chemistry). Currently there are several thousand users all over the world, and the paper describing the method (J. Phys. Cond. Matt. 14, 2745 (2002)) has received more than 6000 citations so far.
pseudo potentials (TM and FHI) are provided in /usr/share/siesta
[ 6.1.2 amd64 ]

http://neutron.ujf.cas.cz/restrax/
by Jan Saroun <saroun@ujf.cas.cz>
License: GPL2
The installation location is /usr/local/simres
[ 1-2011 amd64 ]
http://www-llb.cea.fr/logicielsllb/SpinWave/SW.html
Sylvain Petit, LLB CEA/Saclay
Since the 1950’s, spin wave theory has been of fundamental importance in condensed matter physics. Spin waves are obtained from the linearization of the equation of motion, and can be seen as precession modes of the magnetically ordered structure, with typical energies of a few meV (or THz). Spin wave dispersions are routinely measured by neutron spectroscopy, and provide information about the coupling between spins and magnetic anisotropy parameters.
A spin wave calculating code, SpinWave, has been developed at the Laboratoire Léon Brillouin and is now freely available.
Examples in /usr/share/doc/spinwave
Executable is 'spinwave'
[ 1.0.2 amd64 ]
https://www.ill.eu/vdiffraction
Alain Filhol <vdiffraction@ill.eu>
License: GPL2
[ 3.3 amd64 ]

http://www.helmholtz-berlin.de/forschung/grossgeraete/neutronenstreuung/projekte/vitess/index_en.html
by Klaus Lieutenant <vitess@helmholtz-berlin.d>
License: GPL
The installation location is /usr/local/vitess
[ 0.6 amd64 ]

https://www.ill.eu/users/support-labs-infrastructure/software-scientific-tools/vtas/
by Y. Raoul, A. Filhol, A. Bouvet
License: EUPL
The goal of vTAS is to provide an interactive and graphical display of both the instrument configuration and the corresponding measured space thus making easier the understanding of the behavior of the instrument and its limits.
vTAS supports both the classical TAS geometry and the multiplexed geometry of FLATCONE. Other geometries are available through the vTAS suite described below.
Simulation mode: vTAS allows experimentation with sample parameters, for example the Miller indices of the unit cell, whilst maintaining a representation of the instruments physical state, for example the location of the walls around the instrument, and its angular limits.
The instrument resolution function is computed using the Cooper Nathan's method. A yet untested McStas like Monte Carlo approach is also available but for the bundled version only.
Data viewer mode: vTAS is capable of reading ILL TAS data files. It displays both the data and the corresponding instrument configuration.
Ref.: "The vTAS suite: a simulator for classical and multiplexed three-axis neutron spectrometers"
M. Boehm, A. Filhol, Y. Raoul, J. Kulda, W. Schmidt, K. Schmalzl,
Nuclear Inst. and Methods in Physics Research, A (2013) 697, 40-44.
The installation location is /usr/local/vtas
There are 3 interfaces: vTAS, vUFO and vIMPS
[ 0.2.1 trusty/xenial ]
[ 0.2.1 bionic ]
https://code.google.com/archive/p/wcs2kml/
License: Apache 2
This project consists of an API and several tools for converting FITS images with WCS information into imagery that can be viewed directly in Sky in Google Earth.
The conversion involves warping the input image from its native spherical coordinate system to the lat-long coordinate system and writing out an accompanying KML document describing the location of the image on the sky.
This was compiled from the original wcs2kml source code, with a few patches to adapt to libpng16. Source code is included as well as Makefile in /usr/share/doc/wcs2kml
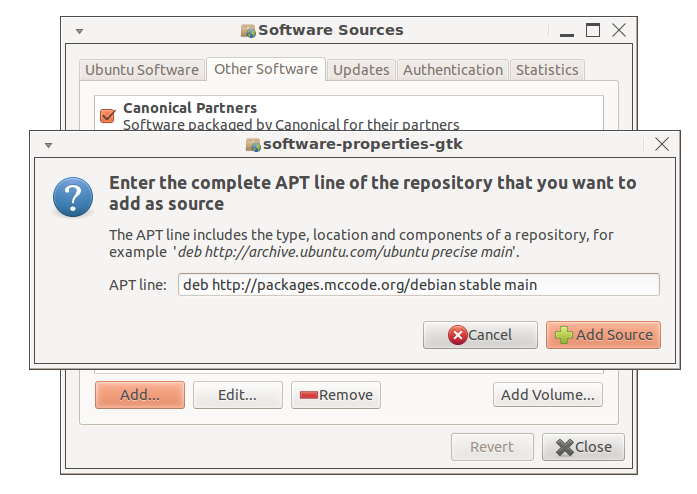 To use this repository, open the Software Sources
settings (from e.g. Synaptic, Ubuntu Software Center or System
Settings) and select the Other Software tab, then press the 'Add...'
button and enter 'deb http://packages.mccode.org/debian stable main'
To use this repository, open the Software Sources
settings (from e.g. Synaptic, Ubuntu Software Center or System
Settings) and select the Other Software tab, then press the 'Add...'
button and enter 'deb http://packages.mccode.org/debian stable main'